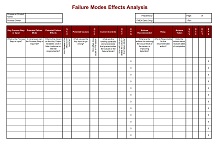
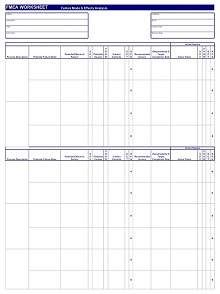
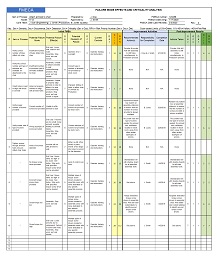
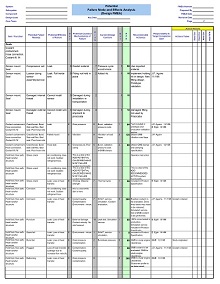
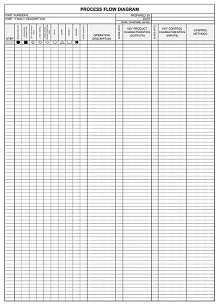
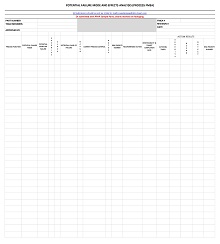
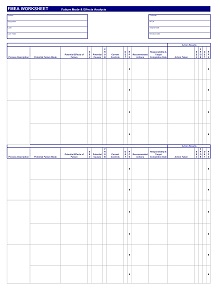
42+ Free Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA) Templates (MS Excel)
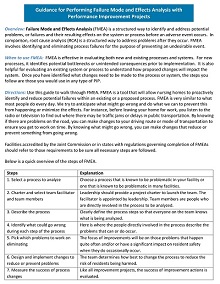
A Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA) Template is a document used to quantify potential risks associated with a given process or activity. This framework helps identify the most important areas that could cause failure, prioritize those risks, and suggest strategies to manage the potential threat. The document consists of measures such as severity, occurrence, and detection of possible threats. It is completed by allowing business leaders to assign scores in each category based on their subjective understanding of an operation or system; these scores can be used to determine which processes require further action or analysis.
Once complete, the FMEA Template serves as a comprehensive reference for evaluating existing risk mitigation methods and determining where additional resource investments will be prioritized. In short, this powerful tool helps organizations assess the viability of a given product or service and make more informed decisions about how best to meet their mission objectives.
Download Free Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA) Templates
Benefits and Limitations of FMEA
Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA) is an important risk management tool that can help organizations plan for and mitigate risks in the products or services they provide. Utilizing FMEA helps teams identify potential failure modes, measure the severity of their effects, identify associated causes and necessary corrective actions, and assess the effectiveness of the proposed solutions. This allows organizations to continuously improve processes and procedures, resulting in better products and experiences for customers.
However, while FMEA can be a powerful tool, it should be approached cautiously since it needs to consider factors like stakeholders’ sensitivity to risk before implementation. To ensure its effectiveness as a risk management strategy, teams must identify timing issues when setting up reviews and objectively assess potential risks. If done properly, FMEA provides an effective way to put measures into place that can help avoid errors. Still, without proper implementation, it runs the risk of contributing to more problems than it solves.
Prioritizing Failure Modes and Determining Corrective Actions
When tackling any problem or issue, it is imperative to prioritize failure modes and determine the corrective actions needed. This process helps pinpoint the root causes of failure and allows you to focus on establishing a plan of action that will fix whatever issues exist. By prioritizing your failure modes, you can establish an organized approach toward dealing with potential pitfalls.
This can include anything from simple tweaks to established procedures to complete infrastructure overhauls. By taking point-by-point steps when addressing systemic failures, you’ll be in a much better position than leaving them until they become unmanageable. Taking appropriate corrective actions early on can help prevent serious future problems and keep operations running smoothly.
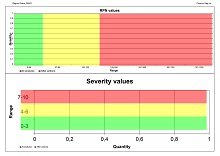
Calculating the Risk Priority Number (RPN)
Calculating the Risk Priority Number (RPN) is essential in ensuring product safety and quality. It allows companies to prioritize potential risks and allocate resources accordingly, making it easier to monitor achievements or losses.
Though choosing the correct RPN can be difficult in some situations, there are certain steps that businesses should take when determining the RPN, such as assessing a product’s severity level, establishing its occurrence frequency, and identifying any existing controls. With this information in mind, companies can calculate the most suitable RPN and assess their products’ possible threats properly.
Guide to Creating a Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA) Template
Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA) is a method of assessing the potential risks associated with a product or process. Using an FMEA template, you can identify potential failure modes, map out their effects, and prioritize preventative actions. In this guide, we’ll provide step-by-step instructions on how to create your own FMEA template.
Identify Your Goal
The first step in creating a Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA) template is to define your goal clearly. Ask yourself what you hope to determine by completing the FMEA analysis. Are you trying to identify potential risks, improve a process, or ensure certain standards are met? Defining your goal upfront will help ensure that the documents you create are tailored to fit your needs.
Gather Relevant Information
Once your goal has been identified, it’s time to gather all the necessary information. This includes relevant data such as customer feedback, previous reports or analyses, processing information from suppliers and manufacturers, etc. Additionally, it’s important to consult with experts with direct knowledge of the product or process being analyzed to get an accurate picture of potential issues.
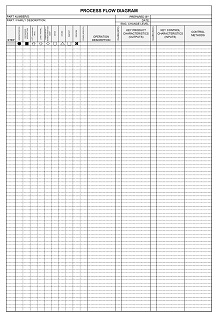
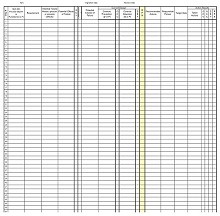
Create a Template
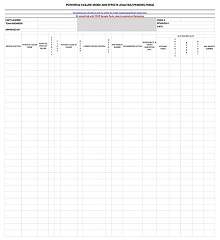
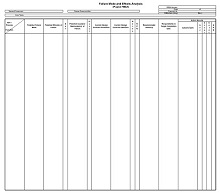
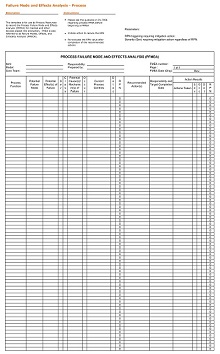
Now, it’s time to create a template for your FMEA analysis. This should include columns for each factor that could potentially cause failure (e.g., design element), its effect on the system (e.g., downtime), and any possible corrective actions (e.g., redesign). It’s important to note that there is no “one size fits all” approach when creating an FMEA template. Every organization has different needs and goals, so adjust accordingly.
Fill Out Your Template
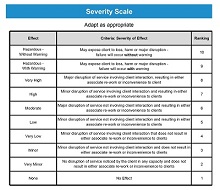
Once you have created your template and gathered all the necessary information for the analysis, it is time for you to begin filling out your template. Start by assigning each factor associated with failure a severity level based on its impact on the system, and this will help determine which items need corrective action first.
After that, assign each factor an occurrence rating, which estimates how often it could potentially fail; this will help identify areas where improvement is needed most urgently. Lastly, assign each factor a detection rating that estimates how easily it can be detected if/when it does fail; this will inform how much monitoring is needed overall during production or service delivery processes.